Illustration by Melanie Peters
Ecommerce sales are growing faster today than ever before. Insider intelligence projects US retail ecommerce sales alone will grow 16.1% in 2022, reaching $1.06 trillion.
Additionally, a 2022 Raydiant study reports that over 56% of consumers prefer to shop online, representing a 10% jump from 2020.
As more customers purchase online, people share more personal and financial data with trusted brands.
Unfortunately, as consumers share sensitive authentication data online, hackers come out of the woodwork to try and steal that data. And, if your company processes payments online, you’re on their hit list.
Perimeter’s 2022 ecommerce benchmark report found hackers aren’t slowing down. Peak malicious login attempts increased by 9.13%, from 84.71% in 2020 to 93.84% in 2021. Even some of the biggest ecommerce companies like Amazon, Bonobos, and Facebook have been victims of data breach cybercrime in the past 18 months.
While consumers continue to shop online, brands and retailers need to understand people will only shop with your company if they trust your site’s security. Baymard found that 18% of users abandoned carts because they didn’t trust the site with their credit card information.
This begs the question: What can you do to prevent cybersecurity breaches and earn the trust of your customers?
Hint: Become PCI Data Security Standard (DSS) compliant.
Table of contents:
- What is PCI DSS?
- Ecommerce PCI compliance checklist
- Ecommerce PCI compliance requirements and levels
- Ecommerce PCI compliance platform types
- PCI compliance FAQ
What is PCI DSS?
PCI DSS compliance stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. It’s an information security standard defined by the Payment Card Industry Security Standard Council, created to improve existing processes, checks, and balances that protect cardholder data.
It applies to any organizations that store, process, or transmit credit card data from places like Visa, Mastercard, Discover, American Express, and JCB.
In December 2004, the main credit card brands formed the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC), the organization behind PCI DSS. Since then, PCI SSC has released several updated versions of the PCI DSS standards. The most recent update—PCI DSS v4.0—was released in March 2022.
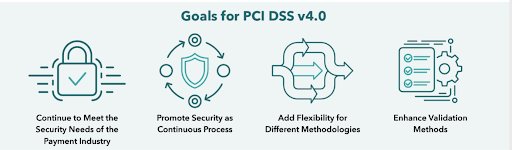
According to a document created by the council, PCI DSS v4.0 incorporates several changes, including:
- Working to continually meet the ongoing security needs of the payments industry by expanding multi-factor authentication requirements and updating password requirements.
- Promoting security as a continuous process to stay ahead of cybercrime. One example includes adding guidance to help people implement and maintain security.
- Increasing flexibility for organizations using different methods to support payment application innovation. This includes the allowance of group, shared, and generic accounts.
- Enhancing validation methods and procedures to support transparency. This includes better reporting.
PCI compliance standards were developed to protect card issuers and cardholders by making sure merchants meet global technical, operational, and security requirements to keep all payment data safe.
Examples of data breaches
The largest data breach in history is attributed to Yahoo!, when, in 2013, Russian spies hacked into the company’s database by sending fake emails to Yahoo! employees and compromised three billion accounts.
Here are some examples of the most recent credit card data breaches in the retail sector.
Next Level Apparel (NLA)
In 2021, Next Level Apparel issued a press release informing customers of a phishing scam. Hackers illegally accessed information, including Social Security numbers, primary account numbers, credit card numbers, and driver’s license numbers. As a result, NLA promised its customers additional security measures and enhanced email security protocols.
Neiman Marcus
Also in 2021, Neiman Marcus discovered a data breach where 4.6 million customer accounts were compromised. Stolen data included customer names, contact info, credit card numbers, user names, passwords, and even virtual gift cards. In response to the data breach, Neiman Marcus issued a mandatory password reset.
2021 Black Friday Cyber Monday (BFCM) hack
During the busiest shopping weekend of the year in 2021, hackers hit 4,151 ecommerce stores due to a “known vulnerability in Magento.” Most of these ecommerce stores were self-hosted on Magento, and hackers accessed personal information and payment information. The UK’s NCSC's Active Cyber Defense program identified the security breach and urged merchants to apply rigid security patches.
Does my business need to be PCI compliant?
You may be wondering whether or not you are required to become PCI compliant. Well, yes and no.
Technically, US federal law doesn’t require PCI compliance, but some states do. Additionally, all major credit card companies require PCI compliance when your organization reaches a certain size.
If you don’t comply, credit card companies may:
- Impose fines (anywhere from $5,000 to $500,000 per month)
- Suspend your credit card usage privileges
- Issue a Common Point of Purchase (CPP) notice
- Hold you liable for fraud charges
“Any retail business that conducts transactions with the major credit card companies is required by those schemes to adhere to the PCI DSS requirements,” says Mitangi Parekh, senior marketing manager at eSentire.
“Retailers have access to credit card data and this data is not just being stored by the retailer in some sort of a locked box. It's transmitted and processed, often with third-party vendors that the retailer may do business with. So, being compliant with the PCI DSS requirements helps retailers determine the necessary controls, policies, or practices they need to have in place to help reduce retail-specific cyber risks,” says Parekh.
Adhering to PCI compliance standards isn’t about avoiding fines. It’s about protecting your customers and their personal data. When you do everything in your power to reduce the potential for data breaches, it increases your business’s credibility and the trust of your customers.
2022 ecommerce PCI compliance checklist
The good news is, if you build your ecommerce store on a SaaS solution like Shopify, your store will automatically be PCI compliant. You won’t have to worry about following rigid steps every year to ensure PCI compliance.
“The best advice for a new ecommerce entrepreneur is to choose a platform that is already PCI compliant, so you’re covered by default. PCI compliance is very pricey, which bigger, more established retailers can invest in, but it’s not practical for small businesses,” says Parekh.
If you choose to invest in a commercial PCI solution or an open-source PCI compliance platform, then your IT team will need to follow these 12 steps. This is a high-level overview, but it’s wise to consult the PCI DSS requirements.
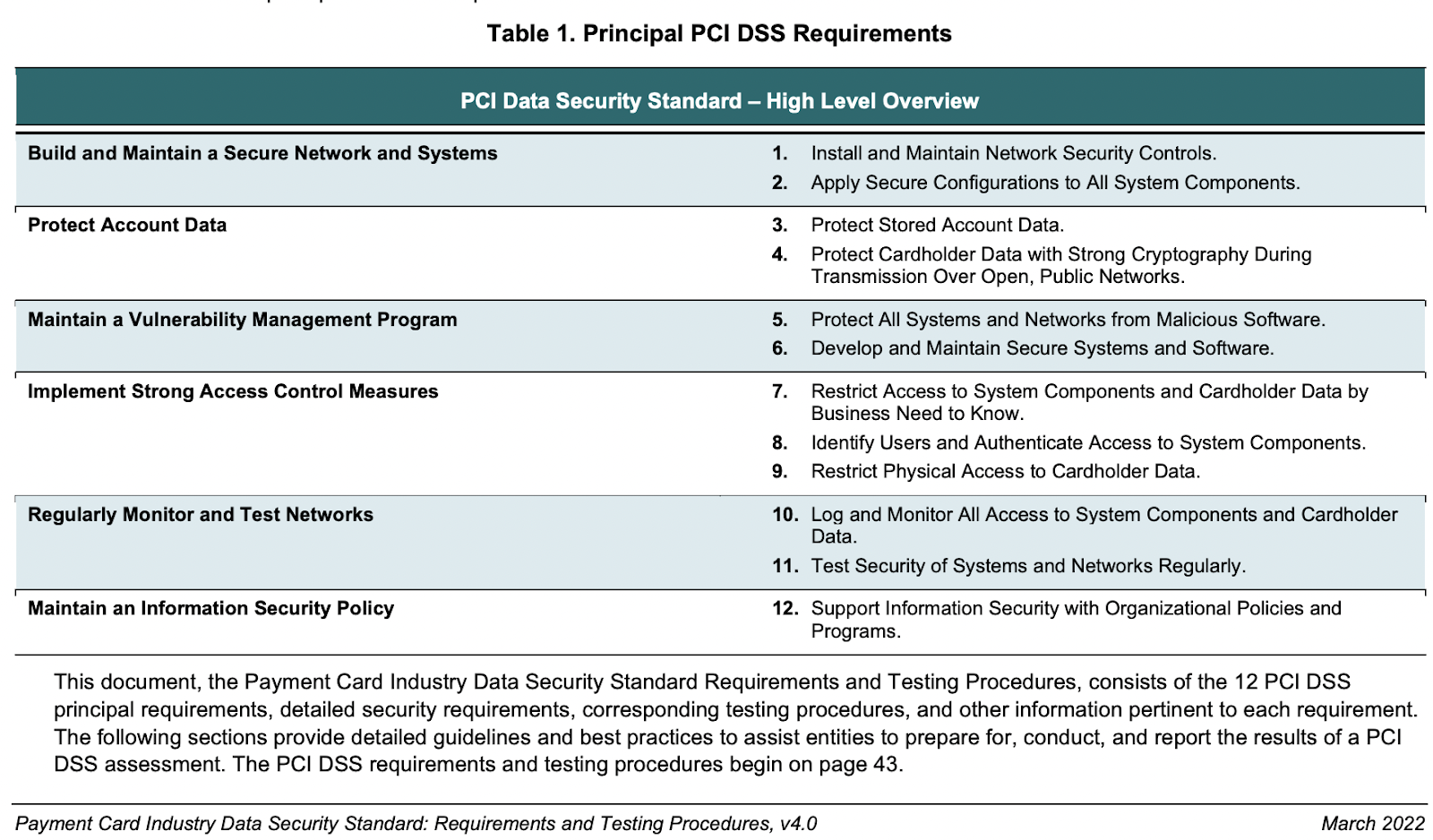
1. Install and maintain network security controls
Installing and maintaining network security controls (NSCs) means installing a firewall to protect cardholder data. This includes only allowing trusted traffic to enter your cardholder data environment (CDE), configuring and maintaining NSCs properly, and creating a highly secure zone for all card data storage.
2. Apply secure configurations to all system components
Hackers often try to breach systems by using default password settings to access sensitive information. Since default passwords are easily determined through public information, make sure you apply secure configurations to system components. Also, change default passwords and make them more secure.
3. Protect stored account data
If you’re storing credit card information or other sensitive data, ensure you have protection methods like point-to-point encryption, truncation, masking, and hashing. Do everything to minimize risks. This includes not storing unnecessary info, truncating cardholder data, and not sending sensitive info through email or instant messaging.
4. Protect cardholder data with strong cryptography
Use strong cryptography to protect data, in particular during transmission over networks that are highly vulnerable to attack—especially public networks.
5. Protect all systems and networks from malicious software
Malware includes things like Trojans, spyware, viruses, worms, ransomware, rootkits, and links. Hackers use these to infiltrate a computer system. Project your cardholders with anti-malware and anti-virus software solutions.
6. Develop and maintain secure systems and software
Avoid hacks with the help of vendor-provided security patches, monitoring your software lifecycle (SLC), and implementing secure coding techniques. Ensure the system components have software patches that protect against compromise and malware.
7. Restrict access to system component data
Make sure critical data is only accessible by authorized systems on a need-to-know basis. Create rules that give specific access and privileges to IT personnel to complete only the necessary tasks.
8. Identify users and authenticate access to system components
Authenticate users by establishing their identity and putting a verification process into place. Consider requiring users to provide proof of identification to verify who they are.
9. Restrict physical access to cardholder data
Protect the transmission of cardholder data by restricting physical access. This means removing hard copies and any other physical document that has sensitive information. If you do need hard copies, restrict the sensitive information.
10. Log and monitor all access to system components and cardholder data
Another critical step in protecting cardholder data is to put logging mechanisms into place and track user activities. Logs on system components help with tracking, altering, and analysis in the event of a breach.
11. Test security of systems and networks regularly
Hackers don’t rest, so don’t sleep on checking the security of your system. Implement tools, processes, and test networks to stress test your security often.
12. Support information security with organizational policies and programs
Take the time to put your security and compliance information in writing. Then, educate all of your employees on what your compliance policies are and how they can play a critical role in protecting your customers’ data.
Ecommerce PCI compliance requirements and levels
Compliance levels vary depending on whether you are a merchant or a service provider. For ecommerce merchants, there are four different compliance levels, and each may vary slightly depending on the credit card scheme.
You can determine your PCI compliance level by evaluating how many transactions you process annually through your respective credit card provider. Here’s a closer look at Visa, Discover, and Mastercard’s compliance levels to help you determine your own.
PCI Compliance Level 1
Level 1 is the highest compliance level. It’s for merchants who process more than six million transactions annually. This level also includes all payment facilitators that process over 300,000 transactions each year.
PCI compliance Level 1 validation requirements include:
- Yearly self-assessment using the PCI SSC SAQ
- Quarterly network vulnerability scans by an approved scanning vendor (ASV) or vulnerability management program
- Attestation of compliance form and submitted documentation
- A Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) to complete an Annual Report on Compliance (ROC) and also a quarterly network scan and attestation of compliance
PCI Compliance Level 2
Level 2 is for merchants who process between one million and six million transactions annually. It also includes payment facilitators that process fewer than 300,000 transactions every year.
PCI compliance Level 2 validation requirements include:
- Yearly self-assessment using the PCI SSC SAQ
- Quarterly network scans by an approved scanning vendor
- Attestation of compliance form and submitted documentation
PCI Compliance Level 3
Level 3 is for smaller ecommerce merchants who process 20,000 to one million transactions each year.
PCI compliance Level 3 validation requirements include:
- Yearly self-assessment using the PCI SSC SAQ
- Quarterly network scans by an approved scanning vendor
- Attestation of compliance form and submitted documentation
PCI Compliance Level 4
Level 4 is for companies that process smaller amounts of transactions annually. Merchants who process fewer than 20,000 transactions a year are considered Level 4.
PCI compliance Level 4 validation requirements include:
- Yearly self-assessment using the PCI SSC SAQ
- Quarterly network scans by an approved scanning vendor
- Attestation of compliance form and submitted documentation
Ecommerce PCI compliance platform types
The question is not whether you need to achieve PCI compliance. You do. The question is: What kind of platform should you use to become PCI compliant?
Just like there are different options for creating, managing, and hosting websites online (e.g., self-hosted, dedicated, or shared), there are also different software options that will help your ecommerce store become PCI compliant.
What you choose will depend on your store size, expertise, budget, IT staff, and goals.
Here are the three main ecommerce PCI compliance platform types and a closer look at how you can be compliant on all three:
- Commercial software
- Open-source software
- Hosted software as a service (SaaS)
Certified commercial PCI software
Buying a certified commercial PCI software is like opting for dedicated hosting for a website.
Instead of paying a hosting company to help you with all the ins and outs of becoming PCI compliant, you buy and maintain your own hardware and commercial software license. With this option, you’re solely responsible for licensing and certifying your store, but commercial PCI software will make it easier.
These certified commercial PCI solution providers are typically reserved for huge and widely recognized ecommerce stores with:
The bottom line: If you’re growing your new ecommerce store, don’t have millions of transactions to manage, or are looking into PCI compliance for the first time, this option is overkill and not for you.
- Level 1 ecommerce compliance
- Well over six million transactions annually
- Robust IT support
- Big budgets to install, customize, and maintain the ecommerce store and PCI compliance requirements
Open-source software
Open-source software for PCI compliance is like WordPress, where you have access to open-source codes and can make your own customizations to enhance security.
With this option, you will pay for your hardware, but you don’t have to worry about paying a software license fee.
Open-source software is a good solution for large ecommerce stores with developers who write their own code but want to automate intake control. In other words, an open-source software will allow your ecommerce store developers to move forward with coding, and rest assured the software will stop non-compliant elements from entering their codebase.
The bottom line: If you are creating a highly customized ecommerce store or app with unique code, instead of building on a platform like Shopify, but don’t have the budget or expertise for a commercial PCI compliance solution, then open-source may be for you.
Hosted software as a service (SaaS)
Using a hosted PCI compliance SaaS solution is like building a site on a shared hosting platform.
Most of the big ecommerce stores (like Shopify) provide hosted SaaS as part of their service. In other words, you can create a Shopify store and don’t have to worry about the security of your site—because PCI compliance is built into Shopify.
“Most ecommerce stores typically don’t need to do anything specific to become PCI compliant simply because if the store is hosted on a platform like Shopify, they will automatically be PCI compliant,” says Parekh.
It is critical to remember, however, that no matter which option you choose (even hosted), you’ll still have to fill out a self-assessment questionnaire if you’re a Level 2–4 merchant. If you’re a Level 1 merchant, you’ll have to fill out the questionnaire and a ROC.
The bottom line: If you’re building an ecommerce store on a commerce platform like Shopify, this option is for you. You don’t have to worry about spending money on hardware or licenses, and you’ll remain PCI compliant with little effort.
Why being PCI compliant is the best thing for your business
Hackers are everywhere in today’s high-tech world, and they are becoming savvier every day. The FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center recently stated there were 2,084 ransomware complaints from January to July 31, 2021, which is a 62% year-over-year increase.
As the internet grows and hackers get better at what they do, it’s critical for ecommerce companies to take action on heightening security.
The way to secure sensitive data and continue to earn the trust of consumers is by following PCI compliance standards.
“Adhering to PCI SSC standards ensures you’ve implemented the best practices to protect against cyber threats and reduce cyber risks impacting retail organizations,” says Parekh. “Furthermore, if you can’t prove that your ecommerce store is PCI compliant, many credit card payment schemes won’t allow you to transmit, store, or even process credit card transactions.”
Above all, growing an ecommerce business requires you to earn the trust of your customers—and you can’t do this if their data isn’t safe with you.
Keep your site secure with Shopify
When push comes to shove, the onus is on you to protect your customers’ credit card information and any other sensitive data.
Unless you are a highly skilled developer with experience in securing ecommerce sites and making sure they are 100% PCI compliant, the best way to protect customer data is with a little help.
In other words, it’s best to rely on help from a hosted SaaS tool (ahem, Shopify) to keep your customers’ credit card data safe. When you set up your ecommerce store with Shopify, you can rest assured it will be PCI compliant.
PCI Compliance FAQ
What does PCI compliance mean?
PCI Compliant means your company is following the Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard and has fulfilled all of the requirements to keep customer data safe.
PCI compliance is a set of requirements designed to ensure the security of credit card information stored on computer systems. These standards were created by the payment industry to help prevent fraud and improve data security.
Does my ecommerce site need to be PCI compliant?
PCI DSS compliance is a requirement for ecommerce stores that keep credit card information, handle any financial transactions, or accept payments using credit cards, debit cards, prepaid cards, and other forms of payment. If you don’t comply, you risk being fined or having your account shut down. Worse, you risk losing your customers’ trust and ruining your company reputation.
PCI compliance affects every aspect of your business, so it’s critical to be PCI compliant.
Am I required by law to become PCI compliant?
You are not required by federal law to have a PCI-compliant website. However, some states do require ecommerce stores to be PCI compliant. It’s worth researching your state or regional government’s requirements to find out what the laws are and how they apply to your business. Additionally, merchants who fail to meet PCI DSS requirements risk being denied payment processor services from their acquirer or acquiring banks due to non-compliance.
How hard is it to be PCI compliant?
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) ensures merchants comply with strict security requirements. These requirements include maintaining secure networks and systems, protecting cardholder data, and implementing strong access control measures.
PCI compliance is incredibly complex, and it involves many detailed steps to get right. The good news is, if you start your store on an ecommerce SaaS platform like Shopify, your site will automatically be PCI compliant.
Where can I find more information on becoming PCI compliant?
This article is a high-level review of how to become PCI compliant. However, if you are going the DIY route to become PCI compliant, the best thing to do is review the official PCI DSS requirements.
What are the 4 PCI Standards?
The 4 PCI Standards are:
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
- PCI PTS (Payment Card Industry PIN Transaction Security)
- PCI P2PE (Payment Card Industry Point-to-Point Encryption)
- PCI SPE (Payment Card Industry Software Security Framework)
What are the PCI compliance guidelines?
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) are a set of guidelines established by major credit card companies to ensure the security of credit card transactions. These guidelines include:
- Maintain a secure network: Install and maintain a firewall to protect cardholder data.
- Protect cardholder data: Encrypt sensitive data to prevent unauthorized access.
- Maintain a vulnerability management program: Regularly scan systems and networks for vulnerabilities and take necessary actions.
- Implement strong access control measures: Restrict access to cardholder data on a need-to-know basis.
- Regularly monitor and test networks: Monitor and test security systems and processes, including tracking and monitoring all access to network resources and cardholder data.
- Maintain an information security policy: Maintain a company-wide information security policy, including training for employees and contractors.
Read More
- What to Do After You've Lost a Loyal Customer
- Cash Flow Management Strategies
- Multi-Channel Customer Acquisition: 7 Tips from $3.7M+ in Ad Spend
- International Ecommerce Strategy: New Tools to Simplify Global Growth for High-Volume Businesses
- B2B Ecommerce Features for Acquiring, Selling & Retaining Customers
- Microcopy: Near Invisible Text That Converts Visitors to Customers (Even When They Don’t Read It)
- Ecommerce Marketing Strategies: A Comprehensive Guide for Growth
- Ecommerce Agency Automation: Saving Time, Selling More & Launching Faster
- How 3 Brands Scaled Their Ecommerce Subscription Model 100-350%






